- The definition of Isometry:
- Basically the distance from an original figure (& it's points) and their transformed figure (& their points).
 |
| An example of how ΔABC's points are equally distanced from ΔA'B'C' points. This is shown by translation. |
- From the types of Transformations only Reflection, Rotation, and Translation are isometries. Dilation on the other hand, is not a isometry.
 |
| This earth figure is isometry b/c each half of the earth is equal distance from the other half. |
- The reason why dilation isn't a isometry is because the original image is either shrunk or enlarged.
 |
| Example of dilation, where ΔABC is dilated by the scale factor of 2. |
- Now you try it, with this question :
What isometry maps figure 1 to figure 3?
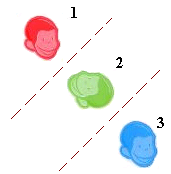
Choices:
A. reflection
B. translation
C. rotation
D. none of these
No comments:
Post a Comment